|
 |
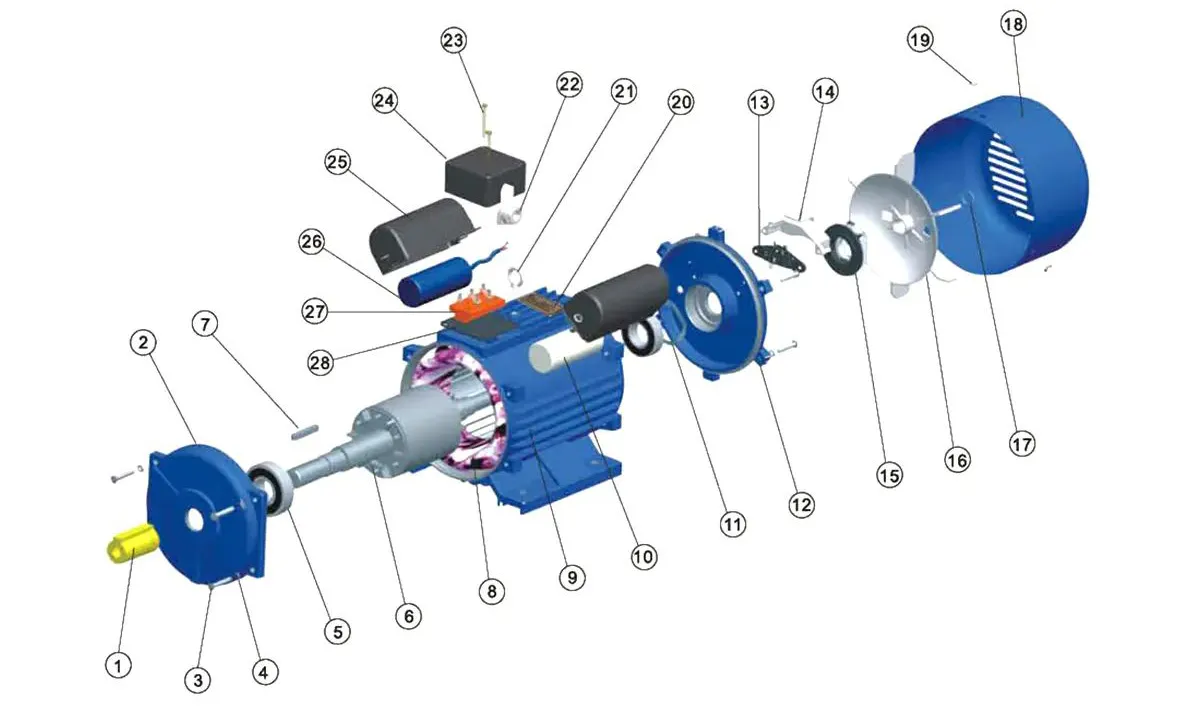
YC Series Capacitors Start Single Phase Motor Parts:
| 1. Shaft cover | 2. Front endshield | 3. Bolt |
| 4. Spring washer | 5. Bearing | 6. Rotor |
| 7. Key | 8. Stator | 9. Frame |
| 10. Capacitor CD60 | 11. Wave form | 12. Rear endshield |
| 13. Backup lane | 14. Shield | 15. Centrifugal switch |
| 16. Fan | 17. Fan clamp | 18. Fan cowl |
| 19. Fan cowl Screw | 20. Nameplate | 21. Eyebolt |
| 22. Jacket | 23. Screw | 24. Terminal box |
| 25. Capacitor box lid | 26. Capacitor CBB60 | 27. Terminal board |
| 28. Leather washer |
YC Series Capacitors Start Single Phase Induction Motor Operating Conditions:
| Ambient Temperature | -15℃ ≤ 0 ≤ 40℃ |
|---|---|
| Altitude | Not exceeding 1000m |
| Rated Voltage | 220V |
| Rated Frequency | 50Hz, 60Hz |
| Protection Class | IP44, IP54 |
| Insulation Class | B, F |
| Cooling Method | IC0141 |
| Duty | S1 (continuous) |
YC Series Capacitors Start Single Phase Induction Motor Technical Data:
| YC Series Heavy Duty Single Phase Induction Motor | ||||||||||||||
| Type | Rated Power | Rated Current (A) | Rated Speed | Efficiency | Power Factor | Rated Torque | Ist/In | Tst/Tn | Tmax/Tn | Noise | Weight | |||
| (kW) | (HP) | 110V | 220V | 240V | (r/min) | (η%) | (cosφ) | (N.m) | (times) | (times) | (times) | dB(A) | (kg) | |
| Synchronous Speed 3000 r/min = 2-poles (50Hz) | ||||||||||||||
| YC711-2 | 0.18KW | 0.25HP | 3.71 | 1.86 | 1.70 | 2800 | 63.0 | 0.70 | 0.6 | 6.5 | 3.0 | 1.8 | 70 | 8 |
| YC712-2 | 0.25KW | 0.34HP | 4.86 | 2.43 | 2.23 | 2800 | 65.0 | 0.72 | 0.9 | 6.5 | 3.0 | 1.8 | 70 | 8.5 |
| YC80A-2 | 0.37KW | 0.5HP | 6.89 | 3.44 | 3.16 | 2840 | 66.0 | 0.74 | 1.2 | 6.5 | 3.0 | 1.8 | 75 | 11 |
| YC80B-2 | 0.55KW | 0.75HP | 10.1 | 5.04 | 4.62 | 2850 | 67.0 | 0.74 | 1.8 | 6.5 | 3.0 | 1.8 | 75 | 12 |
| YC80C-2 | 0.75KW | 1HP | 13.4 | 6.68 | 6.13 | 2850 | 68.0 | 0.75 | 2.5 | 6.5 | 3.0 | 1.8 | 75 | 12.5 |
| YC90S-2 | 1.1KW | 1.5HP | 17.9 | 8.93 | 8.18 | 2850 | 70.0 | 0.80 | 3.7 | 7.0 | 2.5 | 1.8 | 78 | 16 |
| YC90L-2 | 1.5KW | 2HP | 22.8 | 11.4 | 10.4 | 2870 | 73.0 | 0.82 | 5.0 | 7.0 | 2.5 | 1.8 | 78 | 24 |
| YC100L-2 | 2.2KW | 3HP | 33.0 | 16.5 | 15.1 | 2900 | 74.0 | 0.82 | 7.2 | 7.0 | 2.5 | 1.8 | 83 | 34 |
| YC112M1-2 | 3KW | 4HP | 42.7 | 21.4 | 19.6 | 2900 | 76.0 | 0.84 | 9.9 | 7.0 | 2.2 | 1.8 | 87 | 43 |
| YC112M2-2 | 3.75KW | 5HP | 50.2 | 25.1 | 23.0 | 2900 | 79.0 | 0.86 | 12 | 7.0 | 2.2 | 1.8 | 87 | 45 |
| Synchronous Speed 1500 r/min = 4-poles (50Hz) | ||||||||||||||
| YC711-4 | 0.12KW | 0.16HP | 3.92 | 1.96 | 1.80 | 1450 | 48.0 | 0.58 | 0.8 | 6.0 | 3.0 | 1.8 | 65 | 8.5 |
| YC712-4 | 0.18KW | 0.25HP | 5.45 | 2.73 | 2.50 | 1450 | 50.0 | 0.60 | 1.2 | 6.0 | 3.0 | 1.8 | 65 | 9 |
| YC80A-4 | 0.25KW | 0.34HP | 7.05 | 3.52 | 3.23 | 1450 | 52.0 | 0.62 | 1.6 | 6.0 | 3.0 | 1.8 | 70 | 12 |
| YC80B-4 | 0.37KW | 0.5HP | 9.39 | 4.69 | 4.30 | 1450 | 56.0 | 0.64 | 2.4 | 6.0 | 3.0 | 1.8 | 70 | 13 |
| YC80C-4 | 0.55KW | 0.75HP | 12.8 | 6.41 | 5.88 | 1450 | 60.0 | 0.65 | 3.6 | 6.0 | 3.0 | 1.8 | 70 | 15 |
| YC90S-4 | 0.75KW | 1HP | 15.0 | 7.52 | 6.89 | 1450 | 63.0 | 0.72 | 4.9 | 6.5 | 2.5 | 1.8 | 70 | 20 |
| YC90L-4 | 1.1KW | 1.5HP | 20.7 | 10.4 | 9.50 | 1450 | 67.0 | 0.72 | 7.2 | 6.5 | 2.5 | 1.8 | 70 | 24 |
| YC100L-4 | 1.5KW | 2HP | 25.9 | 13.0 | 11.9 | 1450 | 72.0 | 0.73 | 9.9 | 6.5 | 2.5 | 1.8 | 73 | 33 |
| YC112M-4 | 2.2KW | 3HP | 37.0 | 18.5 | 17.0 | 1450 | 73.0 | 0.74 | 14 | 6.5 | 2.5 | 1.8 | 78 | 45 |
| YC132SA-4 | 3KW | 4HP | 44.9 | 22.4 | 20.6 | 1450 | 76.0 | 0.80 | 20 | 6.5 | 2.2 | 1.8 | 87 | 63 |
| YC132SB-4 | 3.7KW | 5HP | 51.9 | 26.0 | 23.8 | 1450 | 79.0 | 0.82 | 24 | 6.5 | 2.2 | 1.8 | 87 | 65 |
| YC132M1-4 | 5.5KW | 7.5HP | 65.4 | 32.7 | 30.0 | 1450 | 85.0 | 0.90 | 36 | 6.5 | 2.0 | 1.8 | 87 | 67 |
| YC132M2-4 | 7.5KW | 10HP | 89.1 | 44.6 | 40.8 | 1450 | 85.0 | 0.90 | 49 | 6.5 | 2.0 | 1.8 | 87 | 70 |
| Synchronous Speed 3600 r/min = 2-poles (60Hz) | ||||||||||||||
| YC711-2 | 0.18KW | 0.25HP | 3.71 | 1.86 | 1.70 | 3360 | 63.0 | 0.70 | 0.5 | 6.5 | 3.0 | 1.8 | 70 | 8 |
| YC712-2 | 0.25KW | 0.34HP | 4.86 | 2.43 | 2.23 | 3360 | 65.0 | 0.72 | 0.7 | 6.5 | 3.0 | 1.8 | 70 | 9 |
| YC80A-2 | 0.37KW | 0.5HP | 6.89 | 3.44 | 3.16 | 3408 | 66.0 | 0.74 | 1.0 | 6.5 | 3.0 | 1.8 | 75 | 11 |
| YC80B-2 | 0.55KW | 0.75HP | 10.1 | 5.04 | 4.62 | 3420 | 67.0 | 0.74 | 1.5 | 6.5 | 3.0 | 1.8 | 75 | 12 |
| YC80C-2 | 0.75KW | 1HP | 13.4 | 6.68 | 6.13 | 3420 | 68.0 | 0.75 | 2.1 | 6.5 | 3.0 | 1.8 | 75 | 13 |
| YC90S-2 | 1.1KW | 1.5HP | 17.9 | 8.93 | 8.18 | 3420 | 70.0 | 0.80 | 3.1 | 7.0 | 2.5 | 1.8 | 78 | 16 |
| YC90L-2 | 1.5KW | 2HP | 22.8 | 11.4 | 10.4 | 3444 | 73.0 | 0.82 | 4.2 | 7.0 | 2.5 | 1.8 | 78 | 24 |
| YC100L-2 | 2.2KW | 3HP | 33.0 | 16.5 | 15.1 | 3480 | 74.0 | 0.82 | 6.0 | 7.0 | 2.5 | 1.8 | 83 | 34 |
| YC112M1-2 | 3KW | 4HP | 42.7 | 21.4 | 19.6 | 3480 | 76.0 | 0.84 | 8.2 | 7.0 | 2.2 | 1.8 | 87 | 43 |
| YC112M2-2 | 3.75KW | 5HP | 50.2 | 25.1 | 23.0 | 3480 | 79.0 | 0.86 | 10 | 7.0 | 2.2 | 1.8 | 87 | 45 |
| Synchronous Speed 1800 r/min = 4-poles (60Hz) | ||||||||||||||
| YC711-4 | 0.12KW | 0.16HP | 3.92 | 1.96 | 1.80 | 1740 | 48.0 | 0.58 | 0.7 | 6.0 | 3.0 | 1.8 | 65 | 8.5 |
| YC712-4 | 0.18KW | 0.25HP | 5.45 | 2.73 | 2.50 | 1740 | 50.0 | 0.60 | 1.0 | 6.0 | 3.0 | 1.8 | 65 | 9 |
| YC80A-4 | 0.25KW | 0.34HP | 7.05 | 3.52 | 3.23 | 1740 | 52.0 | 0.62 | 1.4 | 6.0 | 3.0 | 1.8 | 70 | 12 |
| YC80B-4 | 0.37KW | 0.5HP | 9.39 | 4.69 | 4.30 | 1740 | 56.0 | 0.64 | 2.0 | 6.0 | 3.0 | 1.8 | 70 | 13 |
| YC80C-4 | 0.55KW | 0.75HP | 12.8 | 6.41 | 5.88 | 1740 | 60.0 | 0.65 | 3.0 | 6.0 | 3.0 | 1.8 | 70 | 15 |
| YC90S-4 | 0.75KW | 1HP | 15.0 | 7.52 | 6.89 | 1740 | 63.0 | 0.72 | 4.1 | 6.5 | 2.5 | 1.8 | 70 | 20 |
| YC90L-4 | 1.1KW | 1.5HP | 20.7 | 10.4 | 9.50 | 1740 | 67.0 | 0.72 | 6.0 | 6.5 | 2.5 | 1.8 | 70 | 24 |
| YC100L-4 | 1.5KW | 2HP | 25.9 | 13.0 | 11.9 | 1740 | 72.0 | 0.73 | 8.2 | 6.5 | 2.5 | 1.8 | 73 | 33 |
| YC112M-4 | 2.2KW | 3HP | 37.0 | 18.5 | 17.0 | 1740 | 73.0 | 0.74 | 12 | 6.5 | 2.5 | 1.8 | 78 | 45 |
| YC132SA-4 | 3KW | 4HP | 44.9 | 22.4 | 20.6 | 1740 | 76.0 | 0.80 | 16 | 6.5 | 2.2 | 1.8 | 87 | 63 |
| YC132SB-4 | 3.7KW | 5HP | 51.9 | 26.0 | 23.8 | 1740 | 79.0 | 0.82 | 20 | 6.5 | 2.2 | 1.8 | 87 | 65 |
| YC132M1-4 | 5.5KW | 7.5HP | 65.4 | 32.7 | 30.0 | 1740 | 85.0 | 0.90 | 30 | 6.5 | 2.0 | 1.8 | 87 | 67 |
| YC132M2-4 | 7.5KW | 10HP | 89.1 | 44.6 | 40.8 | 1740 | 85.0 | 0.90 | 41 | 6.5 | 2.0 | 1.8 | 87 | 70 |
YC Series Capacitors Start Single Phase Induction Motor Installation Dimension:
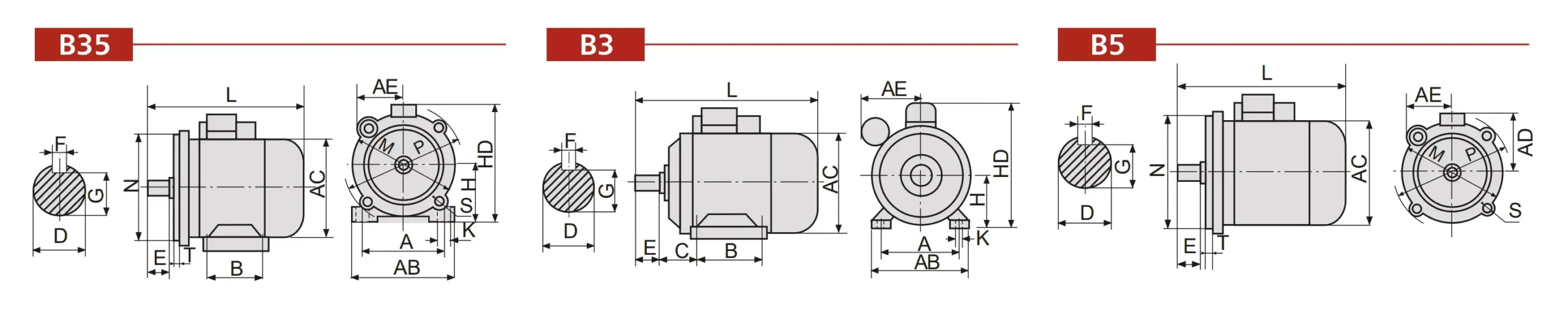
| TYPE | Installation Size | Overall Dimension | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | K | M | N | P | R | S | T | AB | AC | AD | HD | L | |
| 71 | 112 | 90 | 45 | 14 | 30 | 5 | 11 | 71 | 7 | 130 | 110 | 160 | 0 | 10 | 3.5 | 145 | 145 | 140 | 180 | 255 |
| 80 | 125 | 100 | 50 | 19 | 40 | 6 | 15.5 | 80 | 10 | 165 | 130 | 200 | 0 | 12 | 3.5 | 160 | 165 | 150 | 200 | 295 |
| 90S | 140 | 100 | 56 | 24 | 50 | 8 | 20 | 90 | 10 | 165 | 130 | 200 | 0 | 12 | 3.5 | 180 | 185 | 160 | 240 | 370 |
| 90L | 140 | 125 | 56 | 24 | 50 | 8 | 20 | 90 | 10 | 165 | 130 | 200 | 0 | 12 | 3.5 | 180 | 185 | 160 | 240 | 400 |
| 100L | 160 | 140 | 63 | 28 | 60 | 8 | 24 | 100 | 12 | 215 | 180 | 250 | 0 | 15 | 4.0 | 205 | 220 | 180 | 260 | 430 |
| 112M | 190 | 140 | 70 | 28 | 60 | 8 | 24 | 112 | 12 | 215 | 180 | 250 | 0 | 15 | 4.0 | 245 | 250 | 190 | 300 | 455 |
| 132S | 216 | 140 | 89 | 38 | 80 | 10 | 33 | 132 | 12 | 265 | 230 | 300 | 0 | 15 | 4.0 | 280 | 290 | 210 | 350 | 525 |
| 132M | 216 | 178 | 89 | 38 | 80 | 10 | 33 | 132 | 12 | 265 | 230 | 300 | 0 | 15 | 4.0 | 280 | 290 | 210 | 350 | 553 |
YC Series Capacitors Start Single Phase Induction Motor Applications:
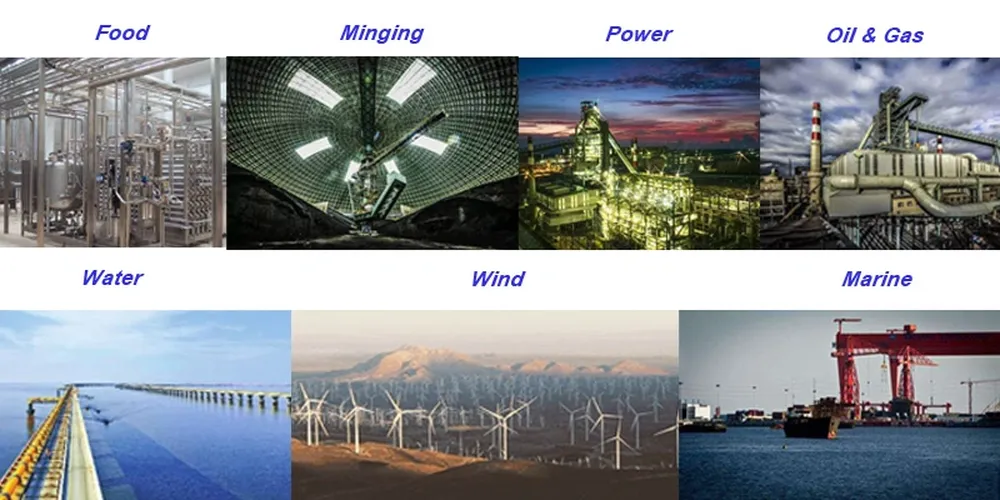

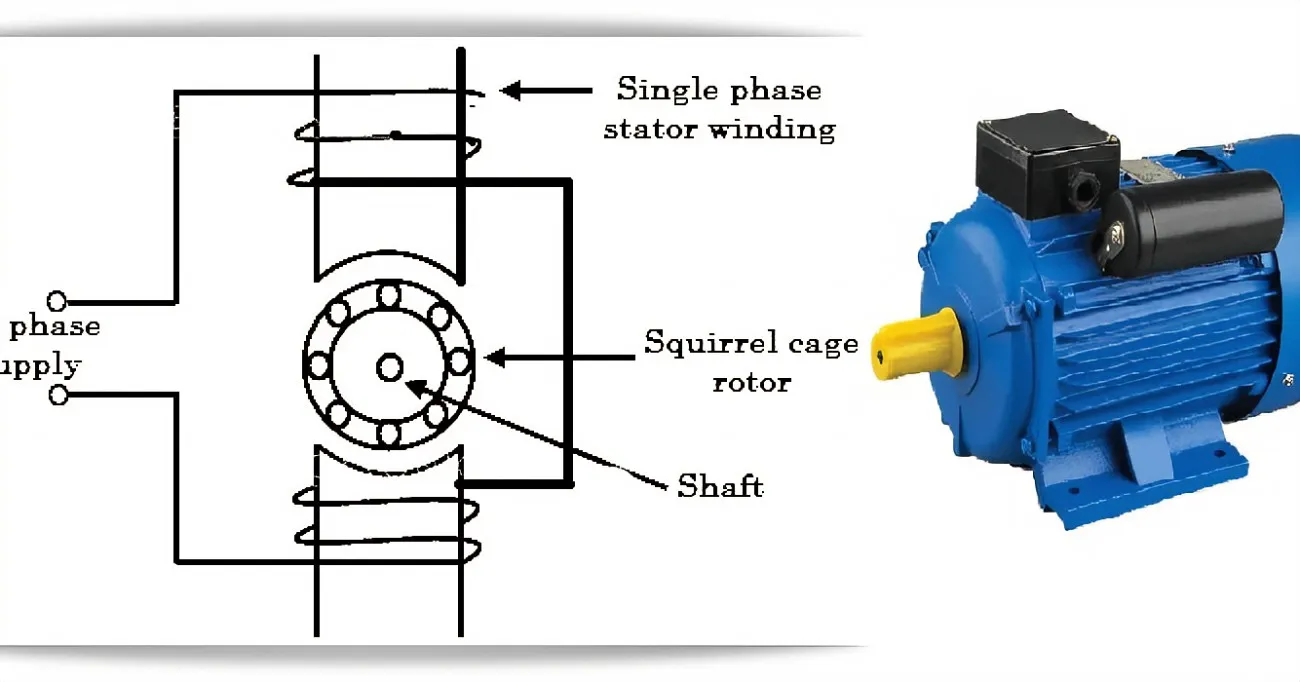
Why Single-Phase Induction Motors Are Not Self-Starting
- Lack of Rotating Magnetic Field
In a single-phase induction motor, the current supplied to the stator produces a pulsating magnetic field rather than a rotating one. This pulsating field cannot create the necessary torque to start the motor. For an induction motor to start, it requires a rotating magnetic field to induce motion in the rotor, but in a single-phase motor, this condition is not met initially. - Absence of Initial Starting Torque
Unlike three-phase motors, which generate a rotating magnetic field as soon as they are energized, a single-phase induction motor does not produce starting torque under normal conditions. The magnetic field in a single-phase motor alternates back and forth, causing the rotor to remain stationary. This lack of starting torque means that the motor cannot begin to rotate by itself. - Effect of the Rotor’s Induced Currents
In a single-phase induction motor, when voltage is applied to the stator, the rotor experiences alternating magnetic fields. However, since the fields are not rotating, the induced currents in the rotor are weak and do not create sufficient torque to start the motor. The rotor simply oscillates, but does not gain enough momentum to start rotating on its own. - Starting Mechanisms for Single-Phase Motors
To overcome this issue, single-phase motors typically require an external starting mechanism. Common methods include using a capacitor, a shaded pole, or a split-phase winding. These techniques are used to create a phase shift between currents in the motor windings, generating a rotating magnetic field or creating the necessary torque to start the motor. - Need for Auxiliary Starting Components
In many single-phase motors, a starting capacitor or a capacitor-run design is employed to temporarily create a rotating magnetic field at startup. Once the motor reaches a certain speed, the auxiliary starting component is disconnected, allowing the motor to run as a single-phase motor. Without these additional components, the motor would not be able to start on its own and would remain stationary.
About FMP
FMP is a national high-tech enterprise specializing in the design, development, and production of advanced motors and electromechanical solutions. We focus on producing YE2, YE3, and YE4 series motors, along with a range of derivative products. Our product offerings also include three-phase and single-phase motors for hydraulic pumps, aluminum-housing motors, non-standard motors for hydraulic pumps, electromechanical integration turbine gear reducers, and other specialized motors.
FMP’s products are extensively used in industrial automation, serving key sectors such as CNC lathes, shoemaking machinery, woodworking machinery, metalworking machinery, plastic machinery, and construction machinery. With a strong commitment to innovation and quality, FMP ensures that all products meet the highest performance standards.
In addition to our comprehensive product range, we are proud to offer custom solutions tailored to the specific needs of our clients. Whether you need specialized motors, non-standard products, or integrated systems, FMP works closely with clients to deliver high-quality, bespoke solutions. Our focus on precision engineering and client satisfaction drives our continued success in global markets.
At FMP, we are dedicated to building long-term, mutually beneficial partnerships, supporting the success of our clients with each project.
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Author: CX