A fluid coupling is a cool tool that helps move power from one spinning part to another using liquid. It has two main pieces: the pump and the turbine. Inside, there are little blades set at special angles to push the liquid around. The pump is connected to the drive shaft, which is the part that gets power from something like an engine. The turbine is hooked up to the driven shaft, which sends the power to whatever machine or thing needs it.
Here’s how it works: when liquid (usually oil) goes into the pump, the drive shaft spins fast and makes the liquid zoom outward because of a force called centrifugal force—it’s like when you spin a bucket of water and it stays inside! The liquid then hits the turbine blades, making the turbine spin too, and that spins the driven shaft. This way, power moves smoothly without the parts touching each other, which keeps things from breaking and makes everything run nice and easy.

If you add a part called a reactor, the fluid coupling turns into something even fancier called a torque converter. The reactor stays still and helps guide the liquid better between the pump and turbine, giving more power when things start moving slowly. This is super helpful in stuff like car engines.
Fluid couplings and torque converters are used in lots of places! In factories, they help run machines like conveyor belts or big rock crushers. On boats, they connect the engine to the propeller so the boat can move through the water. They’re tough, handy, and great for big jobs where you need power to work smoothly!
Fluid Coupling Specifications
Selection power table (KW)
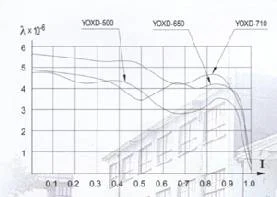
| Technical Data Sheet of Constant Filling Fluid Couplings YOX-Series | λ=f(i) curve for fluid couplings
|
|||||||
| Item no. | 600 (r/min) | 750 (r/min) | 1000 (r/min) | 1500 (r/min) | 3000 (r/min) | Lquid(L) | Weight(KG) | |
| YOX-190 | 0.6-1.1 | 4.5-9.0 | 0.4-0.8 | 8 | ||||
| YOX-200 | 0.75-1.5 | 5.5-11 | 0.5-1.0 | 9.5 | ||||
| YOX-220 | 0.4-0.8 | 1.1-2.2 | 10-18.5 | 0.8-1.6 | 14 | |||
| YOX-250 | 0.7-1.5 | 2.5-5.0 | 15-30 | 1.1-2.2 | 15 | |||
| YOX-280 | 1.5-3.0 | 4.0-7.5 | 37-60 | 1.5-3.0 | 18 | |||
| YOX-320 | 1.1-2.2 | 2.7-5.0 | 7.5-15 | 45-0 | 2.5-5.0 | 28 | ||
| YOX-340 | 1.6-3.0 | 3.0-7.0 | 11-22 | 45-80 | 3.0-6.0 | 30 | ||
| YOX-360 | 2.0-3.8 | 4.5-9.0 | 15-30 | 50-100 | 3.5-7.0 | 46 | ||
| YOX-400 | 3.0-6.0 | 7.5-15 | 22-45 | 80-145 | 4.6-9.0 | 65 | ||
| YOX-420 | 3.5-7 | 11-18.5 | 37-60 | 6.5-12 | 66 | |||
| YOX-450 | 6.1-11 | 14-28 | 40-75 | 6.5-13 | 70 | |||
| YOX-500 | 10-19 | 26-50 | 75-132 | 10-19 | 133 | |||
| YOX-560 | 19-30 | 45-90 | 132-250 | 14-27 | 158 | |||
| YOX-600 | 12-24 | 25-50 | 60-120 | 200-375 | 24-40 | 170 | ||
| YOX-650 | 23-45 | 40-80 | 90-185 | 280-500 | 25-46 | 210 | ||
| YOX-710 | 30-60 | 60-115 | 150-280 | 37-60 | 310 | |||
| YOX-750 | 40-80 | 80-160 | 200-360 | 40-80 | 348 | |||
| YOX-800 | 45-90 | 110-220 | 280-500 | 50-95 | 420 | |||
| YOX-1000 | 140-280 | 270-550 | 70-140 | 510 | ||||
Selection:
To choose the right size fluid coupling with oil, use the technical data sheet and power chart. You’ll need to match it to the motor’s power and speed (the input for the fluid coupling).
When you order, make sure to include the following information about the motor and the machine it’s driving (or the reducer):
- The size of the shaft ends (diameter, fit, or tolerance). If you don’t give specific tolerances, the bores will be made to H7 standards.
- The length of the shafts, and the width and depth of the keys (include the standard number if needed).
If you need a fluid coupling with a belt pulley, brake pulley, or other special features, provide detailed technical information when you order.
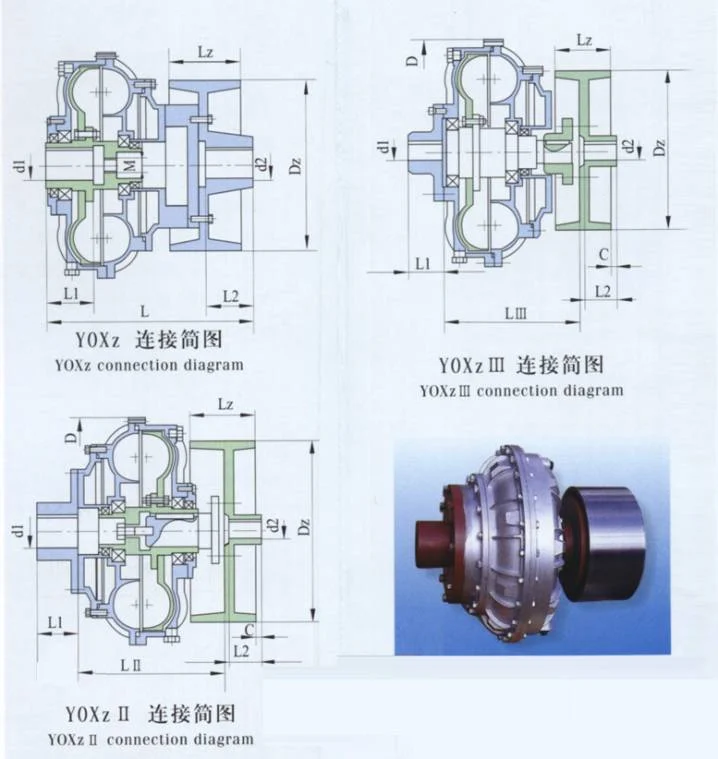
The YOXz fluid coupling is a special machine with a moving wheel at the output point, which connects to an elastic axle coupling (like a plum blossom or elastic pillar type, or one chosen by the customer). There are usually three connection types.
The YOXz is an “inner wheel driver” with a compact design and a smaller shaft size. It’s easy to use, with standard parts that fit many machines. The YOXz’s connection style makes it easy to install or remove without moving the motor or reducer. You only need to remove the weak pillar and unscrew the bolts to take it apart.
When ordering the YOXz fluid coupling, provide these measurements:
- The motor shaft size (d1 and L1).
- The reducer shaft size (d2 and L2).
- The wheel size (Dz, Lz, C). Note: The wheel size in the table is for reference only; the actual size will depend on your needs.
Select Table of YOXz YOXzⅡ YOXzⅢ Fluid Couplings Size and Specification
| Item | D | Dz/Lz | C | d1 | L1 | d2 | L2 | L | LⅡ | LⅢ | M |
| YOX-280 | 328 | 200/85 | 10 | 35 | 80 | 45 | 90 | 300 | 245 | 230 | 20 |
| YOX-320 | 380 | 200/85 | 10 | 40 | 110 | 50 | 110 | 310 | 245 | 280 | 30.5 |
| YOX-360 | 422 | 250/105 | 10 | 55 | 110 | 55 | 110 | 360 | 260 | 300 | 30.5 |
| YOX-400 | 465 | 315/135 | 10 | 60 | 140 | 65 | 140 | 450 | 260 | 350 | 36 |
| YOX-450 | 522 | 315/135 | 10 | 70 | 140 | 70 | 140 | 505 | 280 | 390 | 42 |
| YOX-500 | 572 | 400/170 | 10 | 85 | 170 | 90 | 170 | 575 | 302 | 410 | 42 |
| YOX-560 | 642 | 400/170 | 10 | 100 | 170 | 110 | 170 | 600 | 366 | 440 | 42 |
| YOX-600 | 695 | 500/210 | 15 | 100 | 170 | 130 | 180 | 670 | 380 | 470 | 48 |
| YOX-650 | 745 | 500/210 | 15 | 120 | 210 | 130 | 250 | 725 | 390 | 440 | 48 |
| YOX-710 | 815 | 630/265 | 15 | 120 | 210 | 130 | 250 | 760 | 460 | 560 | 48 |
| YOX-750 | 850 | 630/265 | 20 | 140 | 250 | 150 | 250 | 800 | 520 | 580 | 56 |
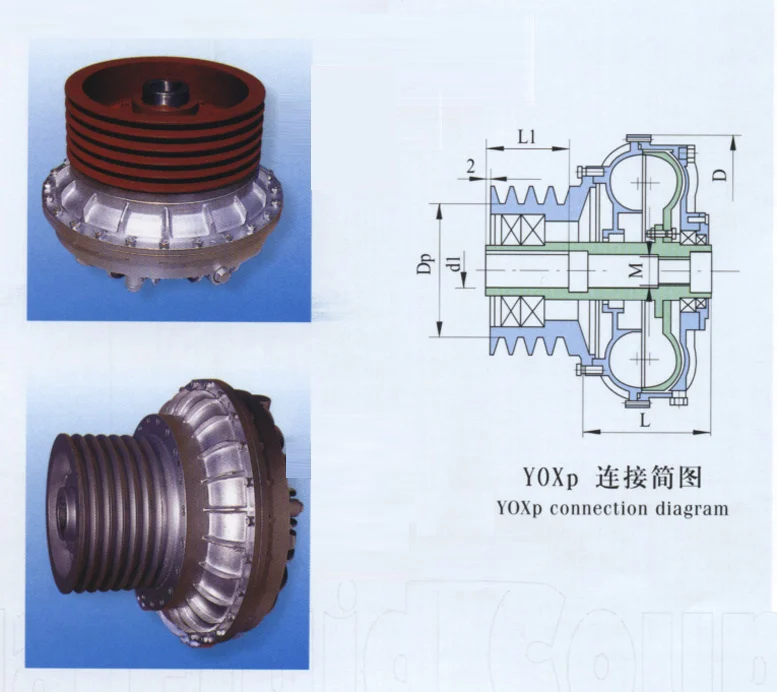
Select Table of YOXp Type Fluid Couplings Size and Specification
| Specification | D | L | d1(max) | L1 | Dp(min) | M |
| YOXp-190 | 235 | 102 | 25 | 60 | 78 | 16 |
| YOXp-200 | 240 | 112 | 25 | 70 | 80 | 16 |
| YOXp-220 | 260 | 175 | 30 | 80 | 80 | 16 |
| YOXp-250 | 300 | 155 | 38 | 80 | 110 | 16 |
| YOXp-280 | 328 | 160 | 38 | 100 | 120 | 20 |
| YOXp-320 | 380 | 170 | 48 | 110 | 130 | 30/font>1.5 |
| YOXp-360 | 422 | 190 | 55 | 120 | 150 | 30/font>1.5 |
| YOXp-400 | 465 | 225 | 65 | 130 | 150 | 36 |
| YOXp-450 | 522 | 240 | 70 | 140 | 200 | 42 |
| YOXp-500 | 572 | 250 | 85 | 170 | 200 | 42 |
| YOXp-560 | 642 | 285 | 100 | 180 | 250 | 42 |
| YOXp-600 | 695 | 330 | 100 | 180 | 250 | 48 |
| YOXp-650 | 745 | 345 | 120 | 210 | 300 | 48 |
Attention: The smallest size of the Dp belt tray and the largest size of the Dl axle hole are important to note.
The YOXp type is a connection style that uses a belt tray with a hydraulic fluid coupling. In this design, the motor axle (or the reducer axle) goes directly into the axle hole of the fluid coupling. This type is best for machines that use belts for power transmission.
When ordering, the customer needs to provide:
-
The size of the motor axle (d1 and L1).
-
The detailed specifications and sizes of the belt tray.
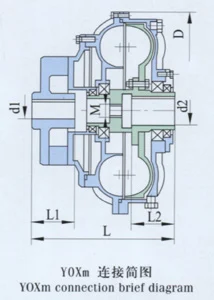
The YOXm type works by having the axle of the reducer (decelerating machine) go directly into the axle hole of the fluid coupling. The motor connects to the fluid coupling using a plum blossom-type elastic axle connector (ML, based on GB5272-85 standards). This connection is simple, reliable, and has the smallest axle size. It is a common type of connection for small fluid couplings.
When ordering, customers need to provide:
- The size of the motor axle (d1 and L1).
- The size of the reducer axle (d2 and L2), as shown in the picture.
If customers don’t provide these details, we will use the standard sizes listed in the table.
 |
 |
Select Table of YOXm Type Fluid Couplings Specification and Size
| Item no. | D | L(min) | d1(max) | L1 | d2(max) | L2 | M(Removal screw hole) | M |
| YOXm-190 | 235 | 180 | 30 | 60 | 25 | 60 | 16 | MT4 |
| YOXm-200 | 240 | 180 | 30 | 60 | 30 | 70 | 16 | MT4 |
| YOXm-220 | 260 | 200 | 36 | 70 | 35 | 70 | 16 | MT5 |
| YOXm-250 | 300 | 210 | 36 | 70 | 40 | 80 | 16 | MT6 |
| YOXm-280 | 328 | 240 | 40 | 80 | 45 | 100 | 20 | MT7 |
| YOXm-320 | 380 | 276 | 48 | 110 | 50 | 110 | 30/font>1.5 | MT7 |
| YOXm-340 | 392 | 282 | 48 | 110 | 42 | 110 | 30/font>1.5 | MT8 |
| YOXm-360 | 422 | 287 | 55 | 110 | 55 | 110 | 30/font>1.5 | MT8 |
| YOXm-400 | 465 | 352 | 60 | 140 | 60 | 130 | 36/font>2 | MT10 |
| YOXm-420 | 480 | 345 | 65 | 140 | 60 | 140 | 36/font>2 | MT10 |
| YOXm-450 | 522 | 384 | 75 | 140 | 70 | 140 | 42/font>2 | MT10 |
| YOXm-500 | 572 | 426 | 80 | 170 | 90 | 170 | 42/font>2 | MT11 |
| YOXm-560 | 642 | 487 | 100 | 210 | 100 | 175 | 42/font>2 | MT11 |
| YOXm-600 | 695 | 540 | 100 | 210 | 100 | 180 | 48/font>2 | MT12 |
| YOXm-650 | 755 | 522 | 130 | 210 | 120 | 210 | 48/font>2 | MT12 |
| YOXm-710 | 815 | 580 | 130 | 210 | 130 | 210 | 48/font>2 | MT12 |
| YOXm-750 | 850 | 603 | 140 | 250 | 140 | 250 | 56/font>2 | MT12 |
| YOXm-1000 | 1130 | 735 | 150 | 250 | 150 | 250 | 56/font>2 |

Attention:L in the table is the smallest axle size.If lengthen the L1,the total length of L will be added.d1,d2are the largest size that we can do.
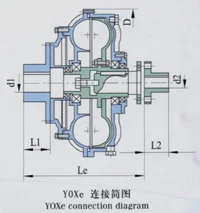
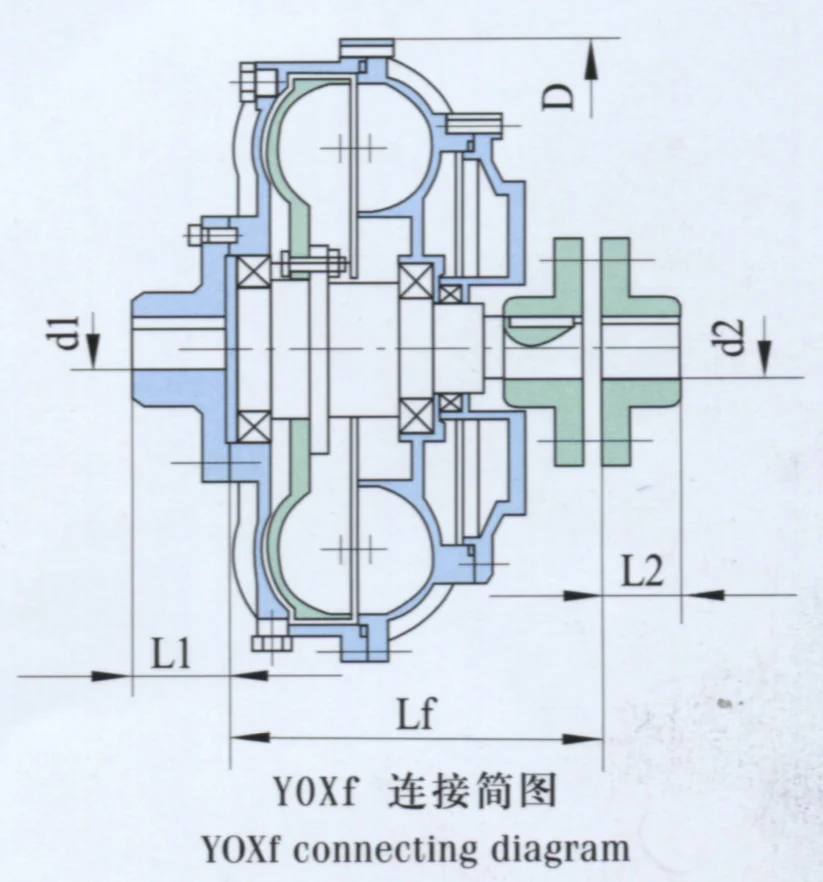
Select Table of YOXe YOXf Fluid Couplings Specification and Size
| Item no. | D | L(min) | d1(max) | L1(max) | d2(max) | L2(max) | Specification of Coupling | |
| Le | Lf | |||||||
| YOXf-250 | 300 | 210 | 210 | 35 | 80 | 35 | 80 | TL4 HL2 |
| YOXf-280 | 328 | 230 | 230 | 35 | 80 | 35 | 80 | TL4 HL2 |
| YOXf-320 | 380 | 300 | 280 | 48 | 110 | 48 | 110 | TL6 HL3 |
| YOXf-360 | 422 | 350 | 300 | 55 | 110 | 48 | 110 | TL6 HL3 |
| YOXf-400 | 465 | 390 | 350 | 60 | 140 | 60 | 140 | TL7 HL4 |
| YOXf-450 | 522 | 415 | 390 | 75 | 140 | 65 | 140 | TL8 HL5 |
| YOXf-500 | 572 | 450 | 410 | 85 | 170 | 85 | 170 | TL9 HL6 |
| YOXf-560 | 642 | 525 | 440 | 90 | 170 | 85 | 170 | TL10 HL6 |
| YOXf-600 | 695 | 550 | 470 | 100 | 170 | 110 | 210 | TL10 HL7 |
| YOXf-650 | 745 | 600 | 440 | 110 | 210 | 110 | 210 | TL11 HL7 |
| YOXf-710 | 815 | 600 | 560 | 120 | 210 | 125 | 210 | TL11 HL8 |
| YOXf-750 | 850 | 650 | 580 | 140 | 250 | 140 | 250 | TL12 HL9 |
| YOXf-800 | 908 | 700 | 580 | 150 | 250 | 160 | 300 | TL12 HL10 |
| YOXf-1000 | 1130 | 750 | 750 | 180 | 300 | 180 | 300 | TL13 HL11 |
The YOXf type connects on both sides and has a longer axle size. However, it has a simple design, which makes it easy to install or fix. You don’t need to move the motor or the reducer. Instead, you only need to remove the elastic pillar and the connecting bolts to take out the fluid coupling.
The elastic axle connector, connection size, and outer size of the YOXf are basically the same as the YOXe type.
 |
 |
Uses of Fluid Couplings
Fluid couplings are used in many machines, such as:
- Belt conveyors, scraper conveyors, and other kinds of conveyors
- Bucket elevators
- Ball mills
- Hoists
- Crushers
- Excavators
- Mixers
- Straighteners
- Cranes
Using fluid couplings for power transmission has several benefits:
- They save energy.
- They protect machines from damage caused by overloading.
- They allow machines to start smoothly.
- They reduce vibration and stress on the equipment.
These benefits make fluid couplings especially useful in heavy industries.
Fluid couplings are also used in ships (marine applications), large ventilators, mixers, and boiler feed pumps. Using fluid couplings can make your equipment last longer and help reduce downtime.