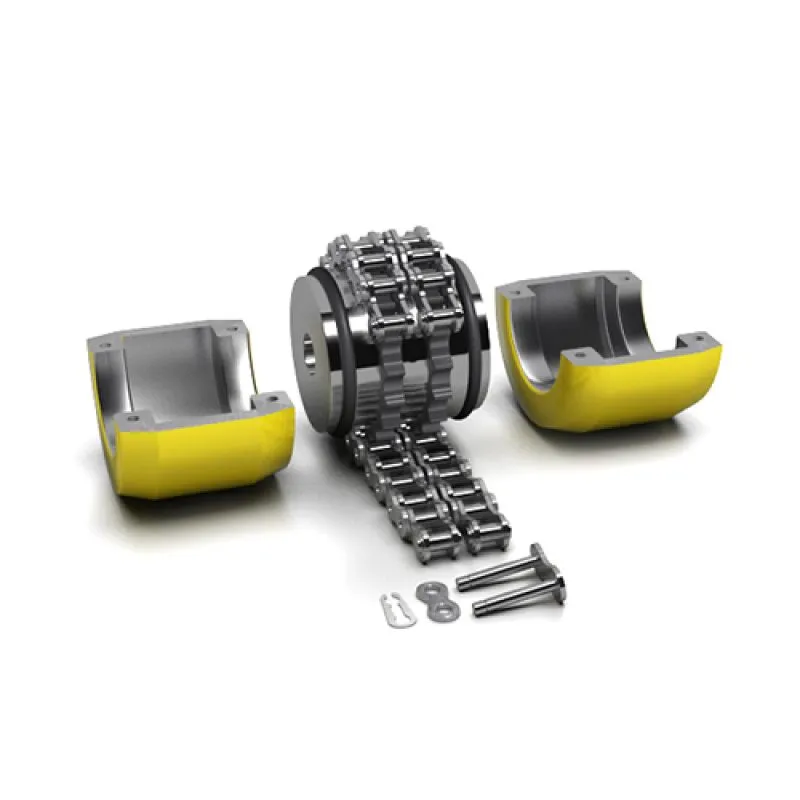
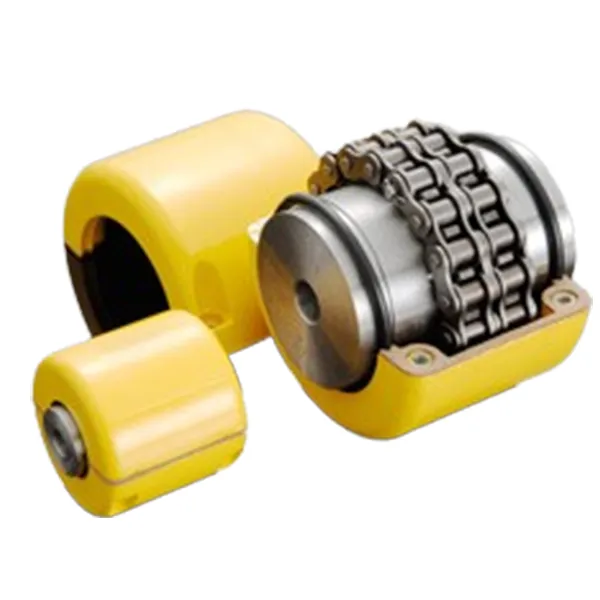
A chain coupling is made up of a double roller chain and two coupling sprockets. The chain joint is used to connect or disconnect the coupling, making it simple and easy to use. Chain couplings are small but very strong, and they are built to last a long time. They are safe and work efficiently, with features that make them easy to install and align, saving time and effort during setup or repairs.
Because of their strong design and flexibility, chain couplings can be used in many ways, such as in machines, conveyor belts, and other mechanical equipment. They are great at transferring torque (a turning force) while handling small misalignments, making them a reliable and useful choice for many jobs.
Parameters of Chain Couplings
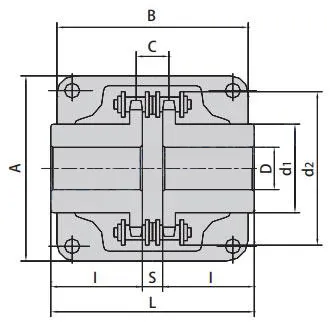
| Chain Coupling No. | Chain No. | Bore Dia | Dimension | Inertia | Approx Weight | Casing | ||||||||
| Min | Max | L | I | S | d1 | d2 | C | ×10-3 | Dimension | Approx Weight | ||||
| A | B | |||||||||||||
| mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | kgf·m2 | kg | mm | mm | kg | ||
| 3012 | 06B-2X12 | 12 | 16 | 64.8 | 29.8 | 5.2 | 25 | 45 | 10.2 | 0.233 | 0.4 | 69 | 63 | 0.3 |
| 4012 | 40-2X12 | 12 | 22 | 79.4 | 36.0 | 7.4 | 35 | 61 | 14.4 | 1.020 | 0.8 | 77 | 72 | 0.3 |
| 4014 | 40-2X14 | 12 | 28 | 79.4 | 36.0 | 7.4 | 43 | 69 | 14.4 | 1.924 | 1.1 | 84 | 75 | 0.4 |
| 4016 | 40-2X16 | 14 | 32 | 87.4 | 40.0 | 7.4 | 50 | 77 | 14.4 | 3.285 | 1.4 | 92 | 75 | 0.4 |
| 5014 | 50-2X14 | 16 | 35 | 99.7 | 45.0 | 9.7 | 53 | 86 | 18.1 | 6.010 | 2.2 | 101 | 85 | 0.5 |
| 5016 | 50-2X16 | 16 | 40 | 99.7 | 45.0 | 9.7 | 60 | 96 | 18.1 | 9.720 | 2.7 | 111 | 85 | 0.6 |
| 5018 | 50-2X18 | 16 | 45 | 99.7 | 45.0 | 9.7 | 70 | 106 | 18.1 | 15.420 | 3.8 | 122 | 85 | 0.8 |
| 6018 | 60-2X18 | 20 | 56 | 123.5 | 56.0 | 11.5 | 85 | 128 | 22.8 | 40.210 | 6.2 | 142 | 106 | 1.2 |
| 6020 | 60-2X20 | 20 | 60 | 123.5 | 56.0 | 11.5 | 98 | 140 | 22.8 | 62.870 | 7.8 | 158 | 105 | 1.6 |
| 6022 | 60-2X22 | 20 | 71 | 123.5 | 56.0 | 11.5 | 110 | 152 | 22.8 | 93.450 | 10.4 | 168 | 117 | 1.8 |
| 8018 | 80-2X18 | 20 | 80 | 141.2 | 63.0 | 15.2 | 110 | 170 | 29.3 | 142.030 | 12.7 | 190 | 129 | 2.5 |
| 8020 | 80-2X20 | 20 | 90 | 145.2 | 65.0 | 15.2 | 120 | 186 | 29.3 | 204.900 | 16.0 | 210 | 137 | 2.9 |
| 8022 | 80-2X22 | 20 | 100 | 157.2 | 71.0 | 15.2 | 140 | 202 | 29.3 | 341.170 | 20.2 | 226 | 137 | 3.6 |
| 10020 | 100-2X20 | 25 | 110 | 178.8 | 80.0 | 18.8 | 160 | 233 | 35.8 | 646.290 | 33.0 | 281 | 153 | 4.6 |
| 12018 | 120-2X18 | 35 | 125 | 202.7 | 90.0 | 22.7 | 170 | 256 | 45.4 | 1075.710 | 47.0 | 307 | 181 | 6.2 |
| 12022 | 120-2X22 | 35 | 140 | 222.7 | 100.0 | 22.7 | 210 | 304 | 45.4 | 2454.500 | 72.0 | 357 | 181 | 8.0 |
Application of Chain Coupling
Chain couplings, known for their ability to transmit high torque while accommodating misalignment, are utilized across various industries due to their durability and flexibility. Here’s a categorized overview of their applications:
1. Industrial Machinery
- Conveyor Systems: Used in manufacturing and material handling to connect motors and rollers, accommodating misalignment and handling heavy loads.
- Pumps and Compressors: Ideal for connecting drivers to pumps/compressors in oil, gas, and water treatment industries, offering reliable torque transmission.
- Steel and Paper Mills: Connect drive shafts to rollers in harsh environments, enduring high torque and temperature variations.
- Crushers/Mills: Handle shock loads in mining and aggregate processing, providing robustness against sudden force changes.
2. Material Handling
- Cranes and Hoists: Ensure precise load movement in construction and shipping, withstanding dynamic stresses.
- Packaging Machinery: Synchronize rollers in high-speed packaging lines, allowing slight misalignment adjustments.
3. Agriculture
- Tractors and Harvesters: Connect power sources to implements in rough terrain, offering durability against dust and debris.
- Irrigation Systems: Link pumps to motors, tolerating misalignment from ground shifts.
4. HVAC and Energy
- Industrial Fans/Blowers: Connect motors to fan shafts in HVAC systems, reducing vibration transmission.
- Moderate-Speed Power Transmission: Used in wind turbines or hydroelectric systems where alignment isn’t perfect.
5. Specialized Applications
- Printing Presses: Synchronize rollers for precise printing, accommodating minor misalignments.
- Marine Auxiliary Systems: Used in propeller shafts or auxiliary machinery, though less common due to corrosion concerns.
Advantages Driving Applications:
- Misalignment Tolerance: Angular/parallel shifts up to 1-2 degrees.
- High Torque Capacity: Suitable for heavy-duty operations.
- Shock Absorption: Dampens vibrations in variable-load scenarios.
- Ease of Maintenance: Simple lubrication and part replacement.
Limitations:
- Not ideal for high-speed applications due to centrifugal forces.
- Regular lubrication needed in contaminant-prone environments.





